Canine Teeth Care: Common Dental Problems in Dogs
Introduction
Our furry friends, dogs, rely on their teeth not only for eating but also for various other activities like playing and exploring. Canine teeth, which are the sharp, pointed teeth in a dog’s mouth, play a crucial role in their overall health and well-being. Just like humans, dogs can experience dental problems that can cause discomfort and affect their quality of life. In this blog, we will explore common dental problems in dogs, their causes, and how to manage these issues to ensure your canine companion maintains a healthy smile.
What are the common dental problems in dogs?
Dogs can experience a range of dental problems, some of which are quite common. These dental issues can cause discomfort, pain, and affect a dog’s overall health. Common dental problems in dogs include:
- Gingivitis: Gingivitis is inflammation of the gums and is one of the earliest signs of dental problems in dogs. It is often caused by the accumulation of plaque and can result in red, swollen, and bleeding gums.
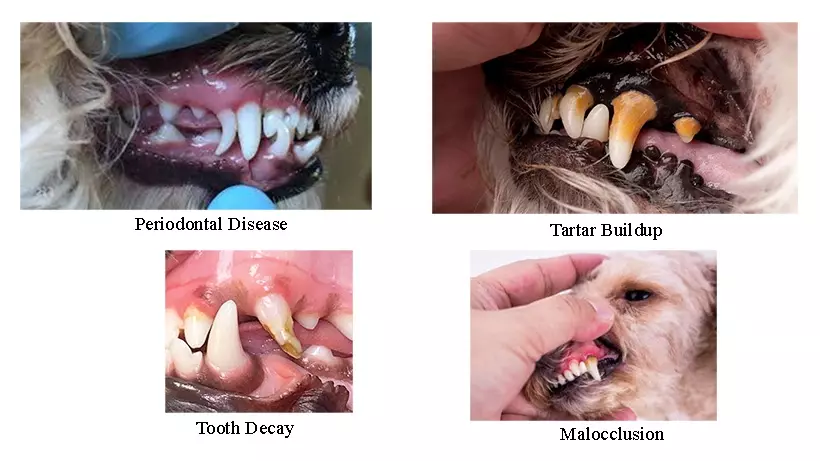
- Periodontal Disease: Periodontal disease is an advanced form of gum disease that affects the tissues supporting the teeth, including the ligaments and bone. It can lead to tooth loss, infection, and severe oral pain.
- Tooth Decay: Just like humans, dogs can develop cavities. This typically occurs in dogs that consume a diet high in sugars and starches or have poor dental hygiene.
- Broken or Fractured Teeth: Dogs can break or fracture their teeth by chewing on hard objects, such as rocks or hard toys. This can expose the sensitive inner part of the tooth, leading to pain and infection.
- Malocclusion: Malocclusion refers to misalignment of the teeth. This can result in problems like overgrown teeth, which may require dental intervention.
- Abscesses: Dental abscesses are pockets of infection that can develop in the gums or around the roots of teeth. They are often painful and may lead to swelling and pus discharge.
- Oral Tumors: While less common, oral tumors can occur in dogs’ mouths, affecting their dental health.
- Plaque and Tartar Buildup: Accumulation of plaque and tartar on the teeth can lead to gingivitis and periodontal disease if not addressed promptly.
- Bad Breath (Halitosis): Foul-smelling breath can be a sign of underlying dental problems, especially if it persists despite good oral hygiene.
- Oral Ulcers: Ulcers in the mouth can be caused by various factors, including trauma, infections, or underlying health conditions.
- Dental Erosion: Erosion of tooth enamel can occur over time, leading to tooth sensitivity and an increased risk of other dental problems.
- Foreign Objects: Dogs may get foreign objects, like plant awns or bone fragments, stuck in their teeth or gums, causing irritation and infection.
What are the causes of dental problems in dogs?
Understanding the causes of dental problems in dogs can help in their prevention and management:
Dental problems in dogs can result from various factors, including genetics, diet, oral hygiene, and overall health. Some of the common causes of dental problems in dogs include:
- Poor Dental Hygiene: One of the primary reasons for dental problems in dogs is a lack of proper dental care. Without regular brushing and dental care, plaque and tartar can accumulate on their teeth, leading to gum disease and other issues.
- Genetics: Some breeds are more predisposed to dental problems due to their genetics. For example, small breeds like Chihuahuas are more prone to dental issues.
- Diet: Poor-quality diets or diets lacking in dental health benefits, such as kibble designed for dental health, can contribute to dental problems.
- Age: As dogs age, their risk of dental problems increases. Older dogs may experience tooth decay, gum disease, and other oral issues.
- Other Health Conditions: Systemic health issues like diabetes can affect a dog’s oral health. Medications for certain medical conditions can also impact dental health.
- Infections: Bacterial infections in the mouth, such as abscesses or gum infections, can lead to dental problems.
- Foreign Objects: Dogs can sometimes get foreign objects, such as plant awns or bone fragments, stuck in their teeth or gums, causing irritation and infection.
How to Manage Dental Problems in dogs?
Managing dental problems in dogs is essential to ensure their oral health and overall well-being. Here are steps to help manage dental problems in dogs:
- Consult a Veterinarian: If you suspect your dog has dental problems, including bad breath, swollen gums, or difficulty eating, consult your veterinarian. They can perform a thorough dental examination, including dental X-rays, to diagnose the issue and create a treatment plan.
- Professional Dental Cleaning: In many cases, professional dental cleaning under anesthesia is necessary to address dental problems effectively. This procedure involves scaling and polishing the teeth to remove plaque, tartar, and calculus. It may also include tooth extractions if necessary.
- Prescribed Medications: Your veterinarian may prescribe antibiotics or pain medications if your dog has gum infections or tooth extractions to manage pain and prevent infection.
- Home Dental Care: To prevent future dental problems, establish a regular home dental care routine for your dog. This can include:
- Toothbrushing: Brush your dog’s teeth regularly with a dog-specific toothbrush and toothpaste. Start slowly and make the experience positive with treats and praise.
- Dental Chews and Toys: Provide dental chews or toys designed to help clean teeth and reduce plaque buildup. Look for products approved by veterinary organizations.
- Dental Wipes or Gels: If your dog resists toothbrushing, dental wipes or gels can be an alternative to help control plaque.
- Dietary Considerations: Some dog foods are formulated to promote dental health. These diets often have a special kibble shape or texture that helps reduce tartar and plaque buildup. Consult your veterinarian for dietary recommendations.
- Provide Fresh Water: Ensure your dog has access to clean, fresh water at all times. Proper hydration is essential for maintaining oral health.
- Monitor for Behavioral Changes: Pay attention to any changes in your dog’s behavior related to eating or chewing. If your dog shows signs of pain or discomfort while eating, contact your veterinarian.
- Address Underlying Health Issues: If dental problems are related to underlying health conditions, such as diabetes or immune system disorders, work closely with your veterinarian to manage these conditions effectively.
- Regular Follow-up: After dental procedures or treatment, follow your veterinarian’s recommendations for follow-up appointments and maintenance care.

How to clean a dog’s teeth and what is the frequency of teeth cleaning in dogs?
Cleaning your dog’s teeth is an essential part of their dental care routine. Here’s how to clean a dog’s teeth and the recommended frequency:
Materials Needed:
- Dog-specific toothbrush or finger brush
- Dog-specific toothpaste (never use human toothpaste)
- Treats or rewards
Steps:
- Introduce Your Dog to Toothbrushing: Before you start brushing, get your dog accustomed to the toothbrush and toothpaste. Allow them to sniff and taste the toothpaste. Make it a positive experience with praise and treats.
- Choose a Quiet Location: Find a quiet, comfortable place for brushing where your dog can relax.
- Apply Toothpaste: Squeeze a small amount of dog-specific toothpaste onto the toothbrush or your finger.
- Gently Lift Your Dog’s Lips: Lift your dog’s lips to expose their teeth and gums. Start with a few front teeth and gradually work your way to the back.
- Brush in Circular Motions: Use gentle, circular motions to brush your dog’s teeth and gums. Focus on the outside surfaces of the teeth, as these are most prone to plaque buildup.
- Be Patient: Brush for a few seconds initially, gradually increasing the duration as your dog becomes more comfortable with the process. Aim for about 30 seconds to 1 minute of brushing per session.
- Reward Your Dog: Always reward your dog with praise and treats after brushing to create a positive association with the activity.
- Rinse the Brush: Rinse the toothbrush or finger brush thoroughly after each use.
Frequency of Teeth Cleaning in Dogs:
The recommended frequency of teeth cleaning in dogs can vary depending on various factors, including your dog’s age, breed, diet, and oral health. Here are some general guidelines:
- Daily or Several Times a Week: Ideally, you should brush your dog’s teeth daily or at least several times a week to effectively prevent plaque and tartar buildup. Daily brushing is most effective.
- Breeds and Size: Smaller dog breeds may be more prone to dental issues, so they may benefit from more frequent brushing. Additionally, some breeds have genetic predispositions to dental problems.
- Age: Dental care becomes more critical as your dog ages, so consider increasing the frequency of brushing as your dog gets older.
- Diet: Dogs on a diet that promotes dental health, such as dental-specific kibble or dental chews, may require less frequent brushing but should still have regular dental check-ups.
- Consult Your Veterinarian: If you’re unsure about the appropriate frequency for your dog, consult your veterinarian. They can assess your dog’s specific needs and provide guidance.
Conclusion
Caring for your dog’s dental health is essential for their overall well-being. Regular maintenance, a proper diet, and prompt attention to any dental issues that arise are crucial for keeping your furry friend’s teeth in tip-top shape. By understanding the common dental problems in dogs and their causes, you can take proactive steps to ensure your canine companion enjoys a healthy smile and a happy life. Remember, a healthy set of teeth contributes to a happier and more comfortable life for your beloved pet.
***If you are a dog parent you must know***
The process teeth eruption in dogs
Just like humans, dogs also go through a fascinating process of teeth eruption during their early stages of life. This natural occurrence is essential for their overall health, nutrition, and overall well-being.
The Timeline of Teeth Eruption:
A dog’s teeth eruption starts when they are just puppies and continues into their early months. Here’s a general timeline:
- Puppy Teeth (Deciduous Teeth): Puppies are born toothless, but they start getting their first set of baby teeth, also known as deciduous teeth, at around 3 weeks of age. These are small, sharp incisors and pointed canine teeth. By 8 weeks, most puppies will have a full set of baby teeth.
- Adult Teeth: As puppies grow, their jaws and bodies develop, and they require stronger, more durable teeth to handle adult dog food. This process usually begins at around 3-4 months and continues until they are 6-7 months old. During this time, the puppy teeth gradually fall out, and the adult teeth emerge.
What to Expect During Puppy Teeth Eruption:
Teeth eruption can sometimes be uncomfortable for puppies and may result in some common behaviors:
- Chewing: Puppies often chew to alleviate discomfort when their adult teeth start coming in. Providing appropriate chew toys can help satisfy this instinct and ease their discomfort.
- Drooling: Excessive drooling may occur as a result of teething. This is entirely normal and usually subsides once the adult teeth are fully in place.
- Gum Sensitivity: Some puppies may experience gum sensitivity during this process. You can gently massage their gums with a clean, soft cloth to provide relief.
Maintaining Dental Health During Teeth Eruption:
Ensuring your dog’s dental health during teeth eruption is crucial for their long-term well-being:
- Regular Check-ups: Schedule a veterinary check-up to monitor the progress of teeth eruption. Your vet can identify any issues early on.
- Proper Diet: Feed your puppy a well-balanced diet appropriate for their age and size. Good nutrition is vital for strong teeth and healthy gums.
- Chew Toys: Offer safe and durable chew toys designed for teething puppies. These toys can help soothe their gums and keep them entertained.
- Brushing: Introduce your puppy to tooth brushing early on. Use a dog-specific toothbrush and toothpaste to maintain good oral hygiene.
- Consult Your Vet: If you notice any signs of discomfort or issues with teeth eruption, consult your veterinarian promptly. They can provide guidance and solutions to ensure your puppy’s dental health.
Common Questions Related to this topic:
What are the common dental problems in dogs?
Common dental problems in dogs include gingivitis, periodontal disease, tooth decay, broken or fractured teeth, malocclusion, abscesses, oral tumors, plaque and tartar buildup, bad breath (halitosis), oral ulcers, dental erosion, and foreign objects stuck in the teeth or gums.
What causes dental problems in dogs?
Dental problems in dogs can be caused by factors such as poor dental hygiene, genetics, diet, age, other health conditions like infections, and foreign objects getting stuck in the teeth or gums.
How can I manage dental problems in my dog?
To manage dental problems in dogs, consult a veterinarian for a diagnosis and treatment plan. This may include professional dental cleaning, prescribed medications, and home dental care, such as toothbrushing, dental chews, and dietary considerations.
How often should I clean my dog’s teeth, and how do I do it?
Ideally, you should brush your dog’s teeth daily or several times a week using a dog-specific toothbrush and toothpaste. Start by introducing your dog to toothbrushing, lift their lips to expose their teeth and gums, and use gentle circular motions while being patient and rewarding your dog afterward.
Can I use human toothpaste to clean my dog’s teeth?
No, you should never use human toothpaste to clean your dog’s teeth. Use a dog-specific toothpaste that is safe for pets.
Are some dog breeds more prone to dental problems?
Yes, some dog breeds, especially smaller breeds like Chihuahuas, are more predisposed to dental problems due to genetics.
What role does diet play in my dog’s dental health?
Diet can impact dental health. Some dog foods are formulated to promote dental health by reducing plaque and tartar buildup. Consult your veterinarian for dietary recommendations.
When should I consult a veterinarian for my dog’s dental issues?
Consult a veterinarian if you notice signs of dental problems in your dog, such as bad breath, swollen gums, or difficulty eating. A veterinarian can perform a thorough examination and create a treatment plan.
What can I do if my dog resists toothbrushing?
If your dog resists toothbrushing, you can consider alternatives like dental wipes or gels to help control plaque. Consult your veterinarian for recommendations.
How can I prevent dental problems in my dog?
To prevent dental problems, establish a regular home dental care routine, provide dental chews or toys, consider dental-specific diets, ensure proper hydration, monitor your dog’s behavior related to eating, and address any underlying health issues that may affect oral health.
